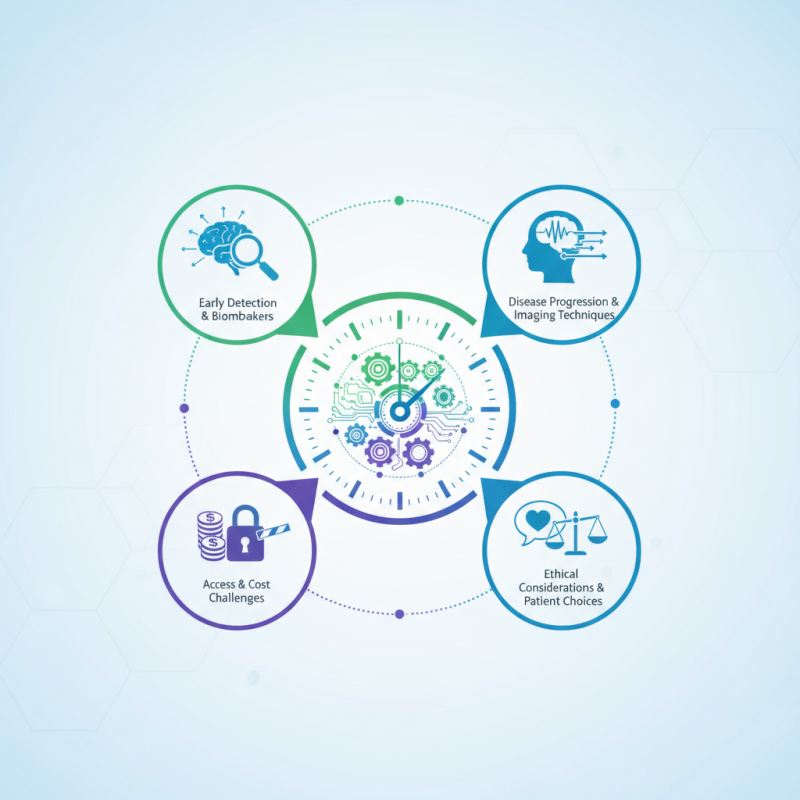
The onset of Alzheimer’s disease remains a pressing concern globally. According to the Alzheimer's Association, an estimated 6.5 million Americans aged 65 and older live with Alzheimer’s. The quest for effective diagnosis tools has led to the rise of innovative technologies, particularly the concept of the "Alzheimer Clock." This metaphorical clock represents a timeline of brain changes leading to Alzheimer’s.
Recent advancements reveal fascinating developments in biomarkers and imaging techniques. Researchers are now able to detect subtle changes in cognition before symptoms arise. The Alzheimer Clock embodies this evolution. It provides insights into the progression of the disease. However, challenges remain. Access to these innovations can be limited due to costs and the need for specialized expertise.
Furthermore, while technologies improve diagnostic accuracy, they also raise ethical considerations. Early detection can lead to difficult choices for patients and families. Balancing hope with the reality of Alzheimer’s disease is complex. Overall, the impact of the Alzheimer Clock on diagnosis is promising. Yet, it necessitates ongoing discussion and reflection within the medical community and society at large.
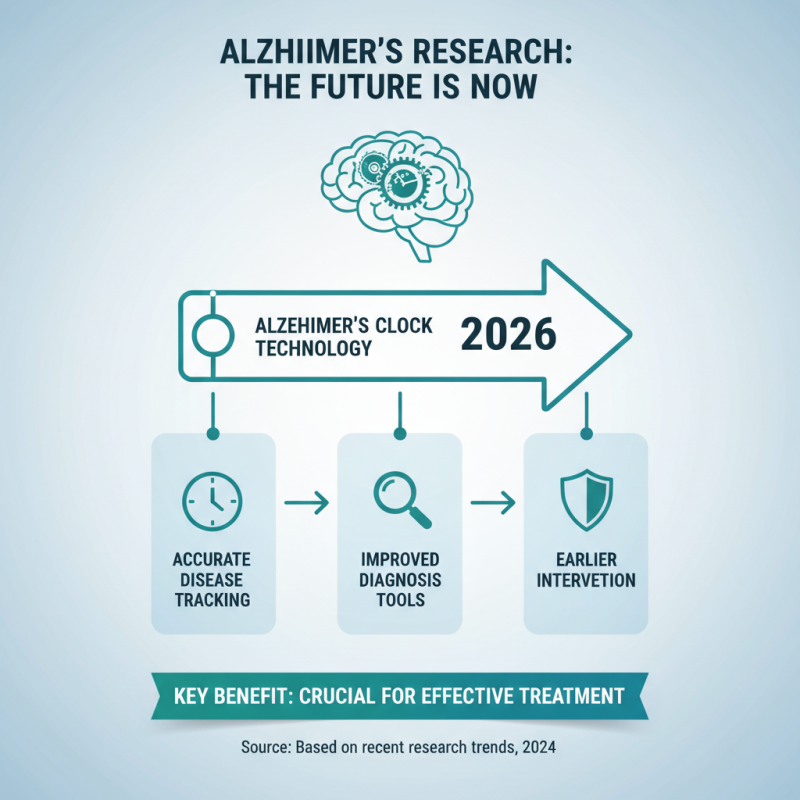
The landscape of Alzheimer's disease research is changing rapidly. In 2026, notable advances in Alzheimer's clock technology show great promise. These innovations help track disease progression more accurately. They provide healthcare professionals with improved tools for diagnosis. This can lead to earlier interventions. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment.
Many new devices now analyze biological markers. They monitor cognitive function changes over time. For example, some clocks utilize AI and machine learning. They can identify subtle shifts in memory and behavior. This data is vital for understanding patient needs. AI can highlight when symptoms may begin to escalate. However, the interpretation of these results can have drawbacks. Variability in individual cases makes a one-size-fits-all approach difficult.
Tips for caregivers and families: Stay informed about these advancements. Understanding technology can help in discussions with healthcare providers. Monitor the patient’s daily changes closely. Small differences may be significant. Lastly, remember that technology is not infallible. Combining tech insights with personal observations offers the best approach. Balancing both perspectives is essential for optimal care.
Innovations in Alzheimer detection are advancing rapidly. Tools that monitor changes in memory and behavior are crucial. These technologies often use wearables to assess cognitive decline continuously. They can alert caregivers about subtle changes in daily activities. This early detection can be a game-changer for families.
Recent developments include apps that analyze speech patterns. Changes in language can signal cognitive issues. It is fascinating yet worrying how technology can unveil these symptoms. However, the accuracy of these tools requires scrutiny. Relying solely on technology may overlook human nuances, like emotional responses or social interactions.
Moreover, some innovations rely on data that might skew results. Ethics around data privacy raise questions. There is a fine line between progress and the potential for misuse. As these innovations evolve, regular feedback from users will be essential. This collaboration can help refine tools and ensure they meet real needs effectively.
Alzheimer Clock technologies are changing the way we diagnose Alzheimer's disease. These innovations provide a more precise measure of cognitive decline. Using advanced algorithms, they analyze patterns in behavior and memory. This enhances diagnostic accuracy. Yet, there are challenges. Not every patient responds in the same way to these assessments.
Some individuals show misleading results. This inconsistency can lead to misdiagnosis. In some cases, patients might appear worse than they are. Others might seem normal but actually have underlying issues. Such variability requires careful interpretation. Clinicians must remain cautious. Diagnosis is not solely a numbers game.
Moreover, these technologies rely heavily on data. The collection and privacy of this data raise ethical questions. How can we ensure that information is secure? These are crucial discussions that need to happen. Balancing innovation and patient rights is essential for progress.
Digital tools are revolutionizing the clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. In 2026, these innovations focus on early detection. They help doctors analyze data more accurately. Smart algorithms can detect subtle changes in cognitive functions. These tools can identify patterns that might be missed during traditional evaluations.
With mobile applications, patients can engage in self-assessments. Tracking symptoms over time becomes easier. However, reliance on technology raises questions. Are patients comfortable sharing their data? Privacy concerns persist. Moreover, not all patients have access to these tools. This could widen the gap in diagnosis and care.
Integration of digital diagnostics requires careful consideration. Training for healthcare providers is necessary. They must understand these tools' limits. While technology can enhance diagnosis, it cannot replace human intuition. Balancing innovation with traditional methods might be key. This dual approach could lead to improved outcomes for patients.
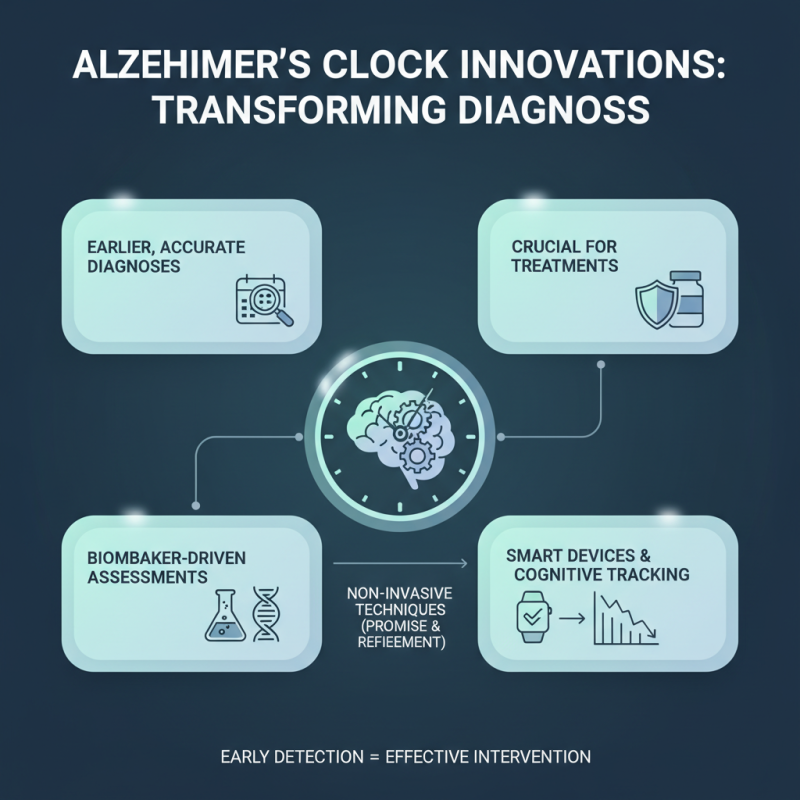
Innovations in Alzheimer's clock technologies are transforming medical approaches. These advancements aim to provide earlier and more accurate diagnoses. Early detection is crucial for effective treatments. New methods are exploring biomarker-driven assessments and smart devices. These tools could help track cognitive decline over time. Non-invasive techniques offer promise but need refinement.
As we look to the future, integration is key. Devices must be user-friendly for patients and healthcare providers. Data management also poses a challenge. How do we securely store and analyze vast amounts of information? There’s room for improvement in patient privacy and consent processes. Each new technology must also consider diverse populations' needs.
Moreover, potential disparities in access to these innovations are concerning. Not everyone may benefit equally from these advancements. Continuous feedback from patients and caregivers is essential. Their insights can shape better and more inclusive solutions. Ultimately, the goal should be to foster innovation responsibly. Balancing technological progress with ethical considerations is crucial for making a meaningful impact.






